Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Aiba, Nobuyuki; Honda, Mitsuru; Kamiya, Kensaku
no journal, ,
We derived a linearized drift MHD equation derived with Frieman-Rotenberg formalism and an incompressible assumption. A linearized drift MHD code, MINERVA-DI, was developed to solve this equation, and has been applied to the stability analysis of MHD modes at tokamak edge pedestal. As the result, it was found that plasma rotation can cancel the well-known stabilizing effect by an ion diamagnetic drift. The impact of plasma rotation on the ion diamagnetic drift effect depends on the ion species due to changing effective mass and effective charge. Based on these understandings, the MHD stability of type-I ELMy H-mode plasmas in JT-60U was analyzed with MINERVA-DI. When the plasma is assumed as static, the MHD stability boundary is far from the operation point observed experimentally, and the ion diamagnetic effect kept the boundary away further. However, by taking into account plasma rotation, the stability boundary shifts close to the operation point even when the ion diamagnetic drift effect is taken into account.
Miyato, Naoaki; Yagi, Masatoshi
no journal, ,
We have performed an ion temperature gradient (ITG) turbulence simulation to investigate effects of the ITG turbulence on the nonlocal transport found in the 4-field reduced magnetohydrodynamics (RMHD) simulation. It is found that the ITG turbulence tends to prevent the nonlocal transport of a kind observed in the 4-field RMHD simulations. The 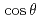 (
( the poloidal angle) component of pressure perturbations, which is very important for the nonlocal transport, is stirred by the ITG turbulence. As a result, the
the poloidal angle) component of pressure perturbations, which is very important for the nonlocal transport, is stirred by the ITG turbulence. As a result, the 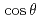 component cannot connect the core region with the edge. On the other hand, the
component cannot connect the core region with the edge. On the other hand, the 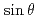 component shows strong geodesic acoustic mode (GAM) oscillations. They are excited by zonal flows nonlinearly generated from the ITG turbulence. We further investigate effects of location of the source/sink on the nonlocal plasma response and the turbulence by the global fluid simulations.
component shows strong geodesic acoustic mode (GAM) oscillations. They are excited by zonal flows nonlinearly generated from the ITG turbulence. We further investigate effects of location of the source/sink on the nonlocal plasma response and the turbulence by the global fluid simulations.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
We develop a kinetic electron model for electrostatic ion temperature gradient driven trapped electron mode (ITG-TEM) turbulence simulations in the Gyrokinetic Toroidal 5D full-f Eulerian code, GT5D. In the model, a full kinetic electron model is used for computing collisional processes and radial electric fields, while turbulent fluctuations are computed by kinetic response of trapped electrons only in order to avoid a high frequency mode, which appear as the electrostatic limit of kinetic Alfv n waves. By using this model, we compare full-f gyrokinetic simulations of ITG turbulence with adiabatic and kinetic electron models, and discuss influences of kinetic electrons on ion turbulent transport.
n waves. By using this model, we compare full-f gyrokinetic simulations of ITG turbulence with adiabatic and kinetic electron models, and discuss influences of kinetic electrons on ion turbulent transport.